Start your journey
"*" indicates required fields

Every web page we visit consumes energy: on average 1.76 g of CO₂e per view, the equivalent of keeping a LED light bulb on for about 2 minutes.
A server consumes on average between 3,000 and 5,000 kWh per year, equal to emissions of about 1–4 tonnes of CO₂e, depending on the energy source and the efficiency of the data centre.
When we think about the factors contributing to climate change, browsing the Internet is probably not the first thing that comes to mind.
Every online activity requires energy, thus contributing to our carbon footprint.
A single server can generate up to 5 tonnes of CO₂e per year, considering both production and energy consumption. Source: Nordic Computer, 2023
Digital technologies are responsible for about 3.9% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Source: Freitag et al., Patterns
One hour of video streaming can emit up to 1 kg of CO₂e, depending on the device and the energy mix. Source: Carbon Trust
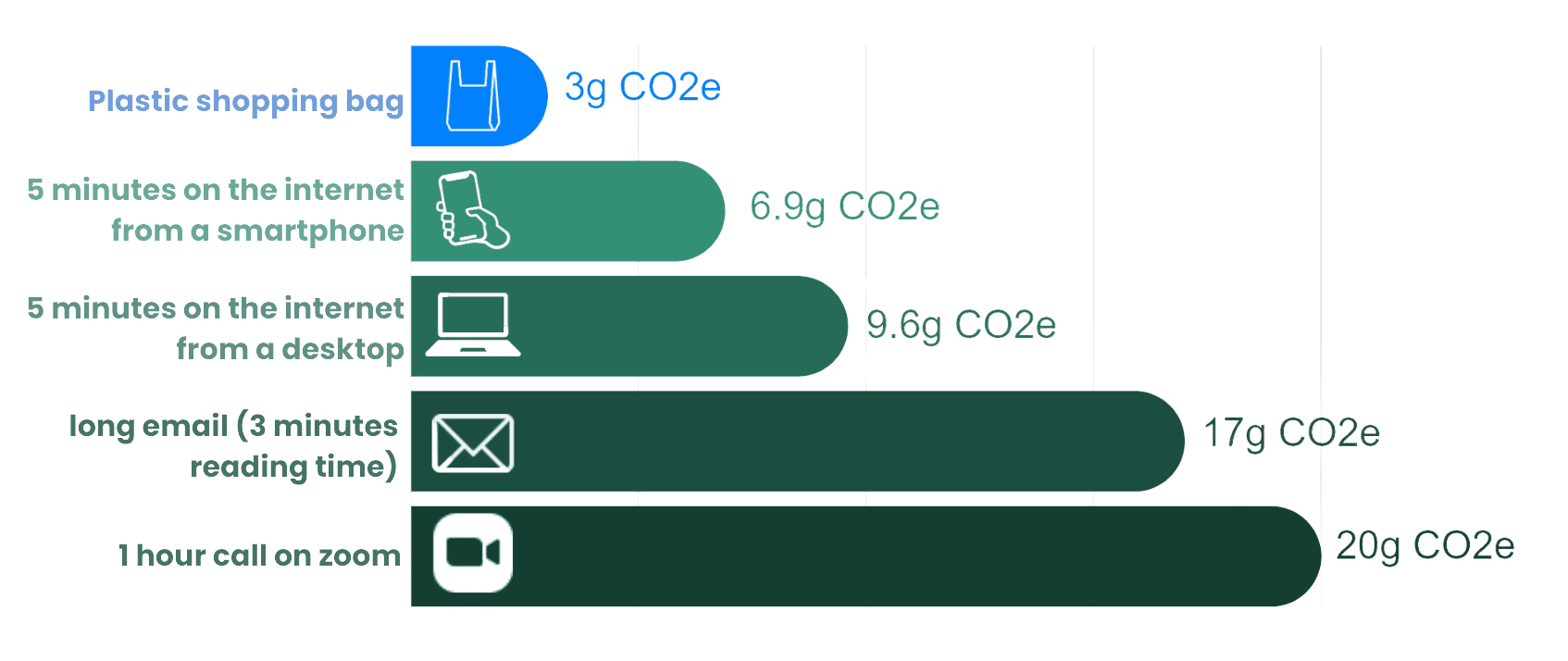
How much do e-mails pollute?
Not all emails are equal in terms of CO₂ equivalent.
Even small actions, such as reducing the number of unnecessary emails sent, can help lower our digital carbon footprint.
Sources: Mike Berners-Lee, How Bad Are Bananas?, Greenoco.io, CarbonCalQlate.com

58% of consumers believe that brands are more influential than governments in shaping a better future.
Source: Edelman Trust Barometer, 2020.

78% of consumers would choose a more sustainable brand even if it means giving up one they already know.
Source: Capgemini, 2020

Website emissions fall under Scope 3 and are among the few categories that a company can directly influence.
Source: GHG Protocol, Scope 3 Standard
Websites of the future
⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀
⠀
The digital sector is responsible for about 3.7% of global CO₂e emissions, a share higher than that of civil aviation. Reducing the environmental impact of a website improves a company’s sustainability and can also enhance online ranking, thanks to better performance and optimised loading times — factors rewarded by search engines.
Sources: IEA 2021; Patterns, Cell Press 2021; Google Search Central
⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀
 ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀
⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀
Start your journey
"*" indicates required fields