The GRI Standards, developed by the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), are a sustainability reporting tool used by organizations worldwide.
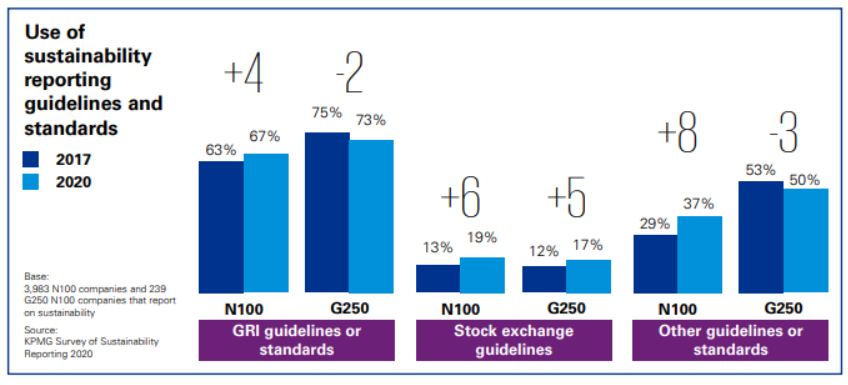
According to a study by KPMG, they are even the most widely used standard for sustainability reports, both worldwide and in Italy, with more than 2/3 of the companies surveyed using them.
But what exactly are they? And why to use them?
GRI Standards: what they are
The GRI Standards provide a comprehensive and transparent framework for sustainability reporting that helps organizations improve their sustainable performance and communicate it effectively to their stakeholders. These standards are designed to be used by all organizations, regardless of their size, sector or geographical location.
The GRI Standards cover a wide range of sustainability issues, including environmental impact, labor rights, human rights protection, social responsibility and supply chain management.
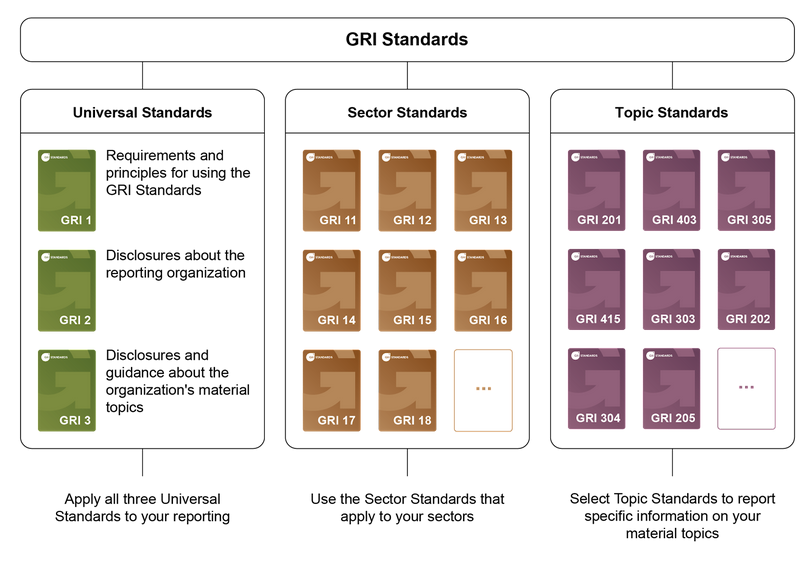
These standards are modular and are divided into 3 macro categories:
- GRI Universal Standards: These are those that apply to all companies and organizations. They cover general and contextual guidance on both the company and the management approach.
- GRI Industry Standards: They aim to increase quality, entirety and consistency of reporting by organizations in specific sectors. Nowadays standards have been developed for 40 sectors, starting with the most impactful such as fuel, agriculture or fisheries.
- GRI-specific (or theme-specific) standards: They include disclosures to provide standards on specific topics such as waste, occupational health and safety, emissions, taxes and biodiversity.
What the GRI standards contain
Within the GRI standards there are 3 types of content:
- Requirements: these are the mandatory instructions. Requirements are indicated in bold type within the documents and are recognisable because they are characterized by the verb “shall/must”. However, an organization may not adhere to the requirements in order to say it is “in line with the standards”.
- Recommendations: these are not mandatory instructions like requirements, but certain conduct is strongly recommended and desirable. In this case the indications are accompanied by the verb “should/may “.
- Guidelines: indications information, examples to help organizations better understand the requirements and how they should be integrated.
GRI 300: Environmental Standards
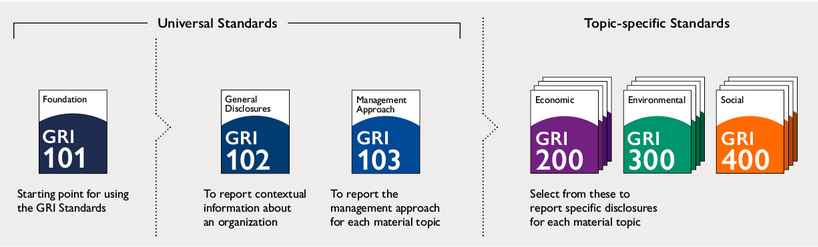
The specific GRI standards can be divided into three broad categories: economic (GRI 200), environmental (GRI 300) and social (GRI 400).
GRI 300 are the environmental standards: raw materials exploitation , use of energy and environmental resources, respect for biodiversity, assessment of pollutant discharges and emissions, environmental compliance, supplier assessment.
In the context of the GRI Standards, the environmental dimension of sustainability concerns the organization ‘s impacts on living and non-living natural systems, including land, air, water and ecosystems.
There are eight environmental standards in the GRI 300 category:
- GRI 301: Materials – management of materials and their impact. Includes information on weight, volume, recycling and reuse
- GRI 302 Energy – management and reporting on energy consumption and its reduction and efficiency
- GRI 303 Water and wastewater – managing and reporting on water abstraction, consumption and discharge and related environmental impacts
- GRI 304 Biodiversity – reporting, preventing, managing and restoring damage to natural habitats caused by the organization ‘s activities
- GRI 305 Emissions – reporting on direct and indirect emissions of greenhouse gasses and ozone-depleting substances. Also includes guidance on managing and reporting on emissions reductions.
- GRI 306 Waste – managing and reporting on waste, its disposal and environmental impacts.
- GRI 307 Environmental compliance – managing and reporting on non-compliance with environmental laws and regulations
- GRI 308 Environmental assessment of suppliers – method of reporting on the environmental assessment of suppliers, both existing ones and in the selection of new ones.
GRI Standards: why adopt them
The GRI Standards have been used by numerous organizations around the world, including large multinational corporations, governmental organizations and non-profit organizations. These standards have also been used by investors and financial institutions to assess the sustainability of organizations and make informed investment decisions.
Organizations that use the GRI Standards for sustainability reporting can reap numerous benefits. For example, these organizations can:
- Improve their sustainable performance, identifying their strengths and areas where they need to improve.
- Improve transparency and communication with their stakeholders, demonstrating their commitment to sustainability and their achievements.
- Facilitate access to sustainability investment funds and increase investor confidence in general.
- Improve the organization’s reputation and image.
- Improve risk management and the ability to make informed sustainability decisions.
The completeness of indications, the modularity of the standards and the possibility of specific indications for one’s own sector or theme have made the GRI standards the most widely used in the world.
Conclusions
In summary, the GRI Standards are an important tool for sustainability reporting by organizations. Whether a company is approaching a sustainability report for the first time, or wants to improve the quality of its reporting, these standards offer a set of guidelines and protocols for collecting and disclosing information that can guide the company towards improvement.
Read also…





